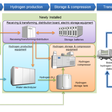
After a successful test, the factory was officially included in the so-called market for the stabilisation of the electricity network. The share of renewable energy sources in the German electrical grid is growing fast and has already reached 33 percent in the beginning of 2015, but this is not without certain inconveniences. Wind and photovoltaic power stations have to deal with surpluses during periods of excess wind and solar power, and these cannot simply be sent to the electrical grid. Major power consumers such as the E-Gas factory in Werlte can increase their production to successfully expend these short-term surpluses of electricity, therefore stabilising the electricity network.
To be accepted in the market for the stabilisation of the electricity network, the factory had to prove that it can draw at least 6 megawatts of electricity from the grid in five minutes. It can also respond to small increases in the production of electricity and effectively nullify their impact on the electricity network.
Audi's factory uses electricity to convert carbon dioxide and water into methane or Audi E-Gas, which is used to power CNG vehicles and in production of other ecological fuels such as E-Diesel and E-Petrol.